painting from the 15th to the 18th century
.jpg)
Jacint Rigau-Ros i Serra, known in French as Hyacinthe Rigaud, was a Catalan-French baroque painter most famous for his portraits of Louis XIV and other members of the French nobility.


The Rohan Master is the name given to an unknown French illustrator in honor of his participation in the work on the manuscript known as the Rohan Clock.
The artist worked in the first half of the 15th century. He is known to have worked as a young man in the Champagne region of France and then moved to Paris around 1415-1420, where he established a large studio and collaborated with other illustrators. His work during this period included not only books of hours but also several secular manuscripts.
The influence of the Parisian artists of the time, Master Boucicault and the Limbur brothers, can be felt in the work of Master Rohan, but his style is characterized by an extraordinary expressiveness.


Iacopo Negretti, best known as Jacopo or Giacomo Palma il Giovane or simply Palma Giovane ("Young Palma"), was an Italian painter from Venice and a notable exponent of the Venetian school. After Tintoretto's death (1594), Palma became Venice's dominant artist perpetuating his style. Outside Venice, he received numerous commissions in the area of Bergamo, then part of the Venetian Domini di Terraferma, and in Central Europe, most prominently from the connoisseur emperor Rudolph II in Prague. Rejecting Mannerism in the 1580s, he embraced a reformist naturalism.[6] He varied the ingeniously synthesised amalgam according to subject matter and patrons' own eclectic and conservative tastes, with "virtuoso skill and a facile intelligence". Palma il Giovane went on to organize his own, large studio which he used to produce a repetitive series of religious and allegorical pictures that can be found throughout the territory of the Venetian Republic.


Jan Victors was a Dutch Golden Age painter mainly of history paintings of Biblical scenes, with some genre scenes. He may have been a pupil of Rembrandt. He probably died in the Dutch East Indies.
He was a conscientious member of the Calvinist Dutch Reformed Church, and for this reason he avoided creating art which depicts Christ, angels, or nudity.
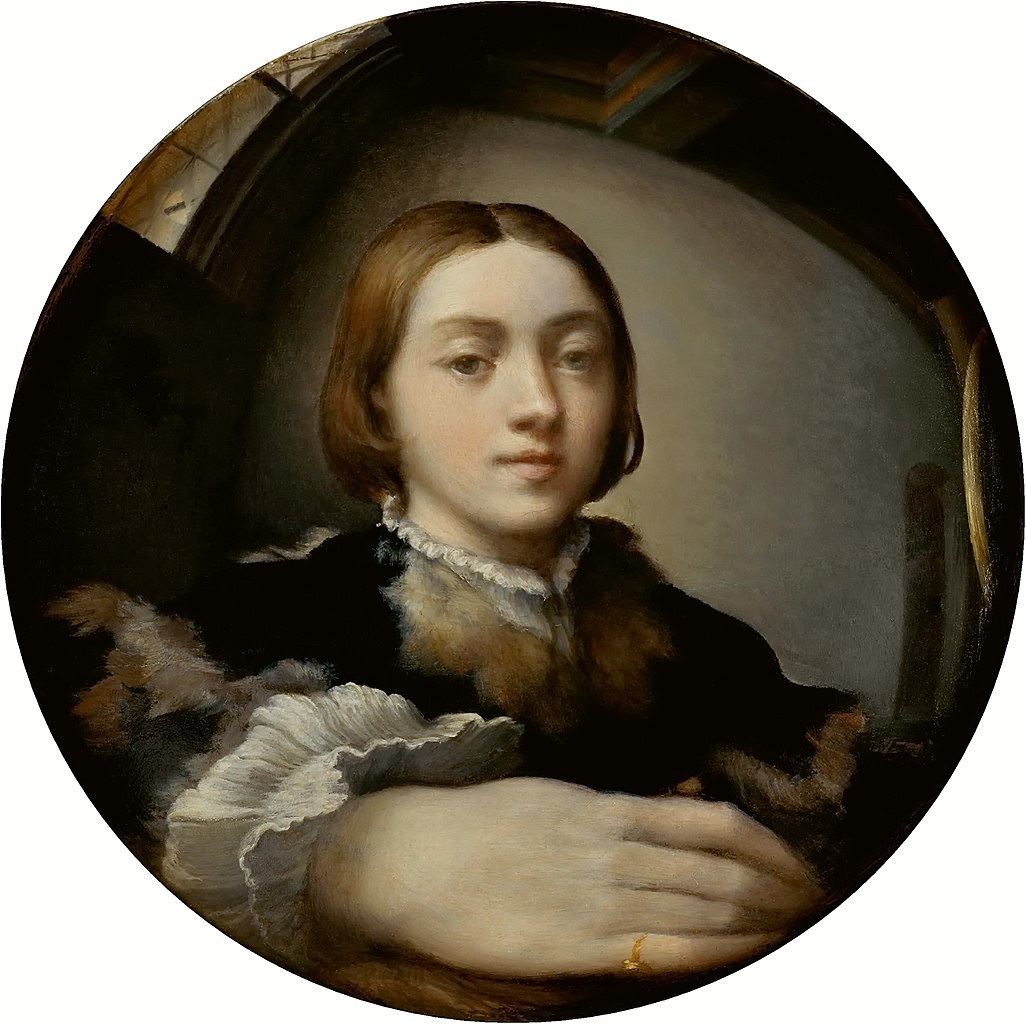


Parmigianino, an Italian Mannerist painter born Girolamo Francesco Maria Mazzola, was a pivotal figure in the development of the Mannerist style, known for his sophisticated and elegant approach to painting. He was a leading figure in Parma's art scene following Correggio and had a significant influence on the artistic developments during the post-High Renaissance period through his expressive and stylish works.
Parmigianino's journey as an artist took him from Parma to Rome and then to Bologna, with his last years spent in Parma. His works, including the renowned "Madonna with the Long Neck," display a unique blend of grace and elegance, coupled with an idiosyncratic use of elongation and distortion, typical of Mannerist aesthetics. This painting, in particular, is noted for its unusual composition and the elongation of figures, embodying the Mannerist style's departure from the proportional norms established during the Renaissance.
He was also an early Italian etcher, utilizing this technique to express the spontaneity of an artist's hand. His etchings and drawings had a considerable influence on printmaking and the visual arts in Italy and Europe. In addition to his paintings, Parmigianino's contributions to the arts include his work in the church of the Steccata in Parma and his innovative approach to integrating painting with architectural elements.
For art collectors and experts, Parmigianino's work represents a critical link between the High Renaissance and the emergence of Baroque and Rococo styles, offering a unique insight into the evolution of European art. His works continue to be celebrated for their originality and mastery, making him a subject of enduring interest in the study of art history.
For those interested in exploring Parmigianino's contributions to art further, subscribing to updates from art institutions or platforms specializing in Renaissance and Mannerist art could provide valuable insights into his life, works, and ongoing exhibitions or sales of his artworks.
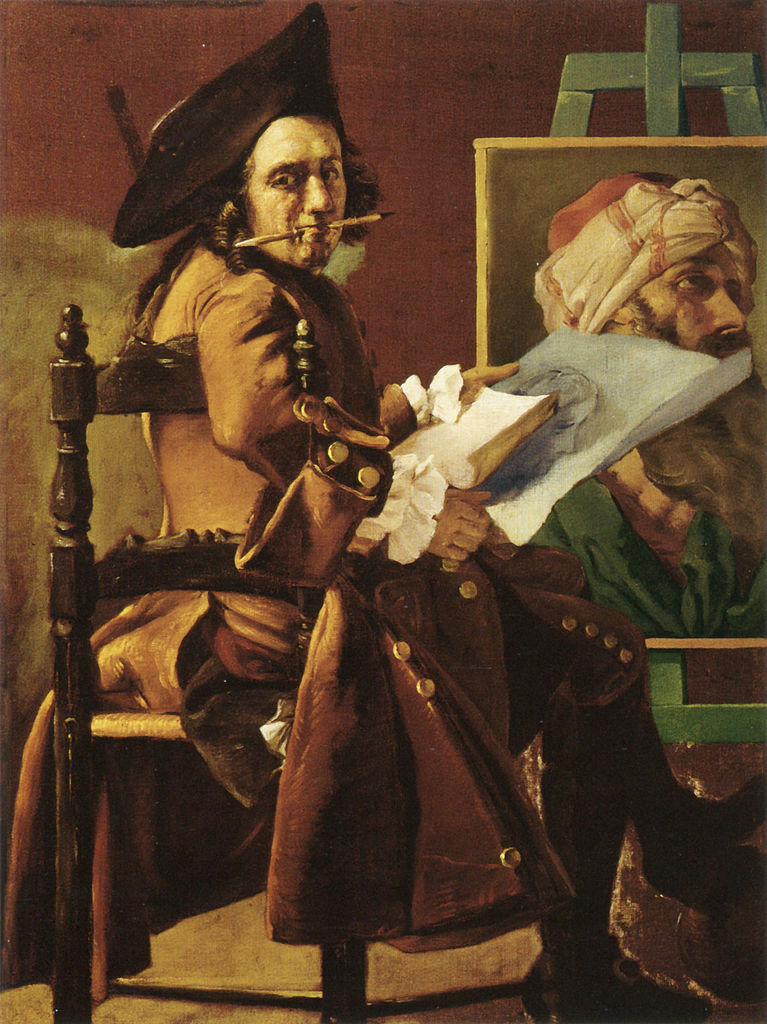


Pierre Subleyras was a French painter renowned for his work during the late Baroque and early Neoclassical periods, mainly active in Italy. Born on November 25, 1699, in Saint-Gilles-du-Gard, France, Pierre Subleyras moved to Rome in 1728 after winning the French Academy's grand prix, a scholarship that allowed him to study in the city. In Rome, he created several significant works, including "Christ's Visit to the House of Simon the Pharisee" and "The Mass of St. Basil," which are celebrated for their detailed depiction and emotional depth.
Pierre Subleyras's paintings were appreciated for their religious themes and portraiture, with his work "The Mass of Saint Basil" being one of his most famous pieces, showcasing his skill in depicting complex religious scenes with emotional resonance. The Metropolitan Museum of Art provides a detailed analysis of "The Mass of Saint Basil," highlighting its historical context and the technical aspects of Subleyras's painting style.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Pierre Subleyras's works offer a glimpse into the transition between the Baroque and Neoclassical periods, reflecting the cultural and artistic shifts of the 18th century. His paintings can be found in various prestigious museums, including the Louvre and the State Hermitage Museum.
To stay updated on news and events related to Pierre Subleyras and his works, consider subscribing for updates. This way, you'll receive notifications about new product sales and auction events featuring Pierre Subleyras's art, ensuring you don't miss out on opportunities to engage with the legacy of this influential painter.